As a construction industry consultant, I’m frequently asked, “What number should I use to mark up my costs?” The simple answer is “Whatever will cover your overhead and provide the target profit you want.”
Mistake #1: Confusing Markup and Margin
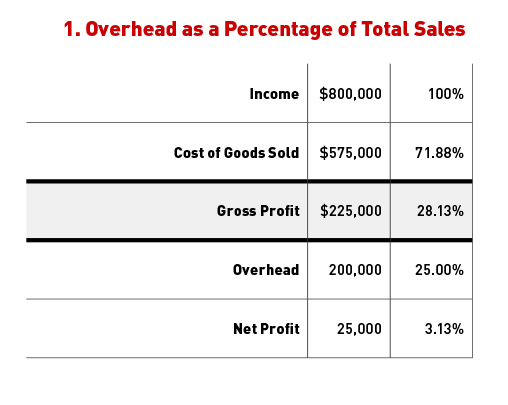
A common mistake is to look at total overhead for a given period (say 12 months) and express it as a percentage of total sales for that period. For example, here’s a company with $800,000 in sales, less production and overhead costs. Dividing each amount by the total sales figure gives us the results shown in the right-hand column.
Starting with the 100% figure for sales, this company is losing 71.88% (or $.7188 on a dollar) to produce the work, and another 25% (or $.25 on a dollar) for overhead, leaving 3.13% (or $.0313 on a dollar) profit. Many contractors look at that and say, “OK, I need to take my costs and add 25% for overhead.” If they’re happy with the amount of profit they made in the past, they would probably try to perpetuate the strategy by adding another 3.13% for profit.
Let’s imagine, then, that the contractor by sheer coincidence happens to sell a single big job and he estimates the costs will be exactly $575,000. Let’s see what happens when he adds the 25% + 3.13% to the estimated costs. He should end up with a sale price of $800,000. What happened?
Remember that in the original Profit and Loss, all the line numbers (Cost of Goods Sold, Gross Profit, Overhead, Net Profit) were compared with total sales. Later, when our contractor was trying to price a new job, he added 25% and 3.13% based on the estimated costs of the job. Our contractor confused markup with margin. The terms are easily confused (they even sound similar), but markup always compares against costs, while margin is compared against selling price.
Mistake # 2: Using Multiple Markups Without Blending Costs
Contractors, particularly those who sell T&M work and are put in a position of explaining (or too often, justifying) their pricing to customers, frequently grapple with how to mark up different types of costs. For example, I often hear from contractors that “the subcontractor is doing all the work, so it doesn’t seem fair to add much of a markup on top of that.” Or, “I can justify marking up the little stuff like lumber and fasteners by 40% to 50%, but when it comes to $50,000 worth of cabinets, how can I possibly keep the same markup?”
The truth is that no matter how you arrive at the selling price of a job (or how much you add to individual line items in a T&M invoice), if you don’t sell the work for the correct markup for your company, you will not thrive and grow; you may not even survive. That said, there are many ways to arrive at that magic sales price (for a contract price job) or markup (for T&M work).
The first thing to understand is that unless you apply a uniform markup to all calculated costs consistently, you will need to blend, or mix, costs. Take, for example, a contractor who has identified his burdened hourly cost for field labor. He is selling a contract price job by applying a 50% markup to all costs. Notice that no matter what percentage of the job cost is for labor, materials, or subs, the selling price remains the same.
But let’s say that the contractor prefers to apply variable markups to the different cost categories. Let’s say that he puts a 100% markup on labor and a 25% markup on subs and materials. (These are the markups required in order to match the $150,000 selling price arrived at by applying a uniform markup to all costs.) How will varying percentages of these costs affect the selling price? Depending on the type of job, the sales price changes. (Next month I’ll go into greater detail about how to blend markup to make this work.)
Mistake #3: Misunderstanding ‘Break Even’
I haven’t yet met a contractor who didn’t admit to selling a job at a price that he knew was too low. There’s always a rationalization: “I had to take it to keep the guys working” or “the job was right on Main Street; it was like free advertising” or “I made a ton of money on the last job and this one had some interesting challenges.”
The misunderstanding occurs when contractors assume that “break even” refers to charging enough for the job to cover the actual costs of the job. The logic error here is to forget that the sale price must cover not just the job costs, but also overhead, with enough left over to contribute to profit.
Let’s look at five identical “good” jobs, where “good” means that there was adequate gross profit to cover that job’s share of company overhead and contribute to total profit.
What happens when a job “breaks even”? If you think that “break even” means that costs equal sale price, you do not break even, you’re actually in the hole by $2,500. That’s because overhead costs keep coming in regardless of how you’ve priced your job.
True “break even” refers to a price that covers both the production costs and that job’s fair share of company overhead. There is nothing left to contribute to profit, but at least overhead is covered.
Conclusions
There are only three ways to increase your true bottom line (profit):
1. Reduce your overhead so gross profit dollars go further and, after covering overhead, “fall into” your net profit.
2. Reduce production costs by sticking to your schedule, cutting back on waste, and improving efficiency through increased oversight, training, and accountability.
3. Raise your prices. This has zero impact on the production process or what you spend on overhead or production costs. Any dollars that you add to the selling price will, under most conditions, fall directly to your net profit.